Cloned Genes and Production of Growth Hormones, Vaccines and Commercial Chemicals
In the human body, peptide hormones are secreted after encoding by peptide hormone genes in the specialized cells, for instance insulin and other Human Growth Hormones (hGH).
Insulin
This peptide hormone i.e. insulin is secreted by the Islets of Langerhans of pancreas which catabolizes glucose in blood. Insulin is a boon for the diabetics whose normal function for sugar metabolism generally fails.
Insulin consists of two polypeptide chains, chain A (21 amino acid long) and B (30 amino acid long). Its precursor is proinsulin which also contains two polypeptide chains, A and B, and is connected with a third peptide chain-C (35 amino acid long). However, the recent discoveries reveal that precursor of insulin is pre- pro insulin which is about 109 amino acids long. The pre-pro- insulin is synthesized in beta cells of pancreas, the structure of which is given below :
NH2-(Peptide)-b-Chain- (peptide-c)- A chain-COOH
In the beginning, efforts were made to isolate mRNA for pre- pro- insulin from rats Islets of Langerhans of pancreas and to synthesize cDNA. Thereafter, it was inserted into a plasmid. The recombinant plasmids were transferred into the E. coli cells which secreted pro-insulin.
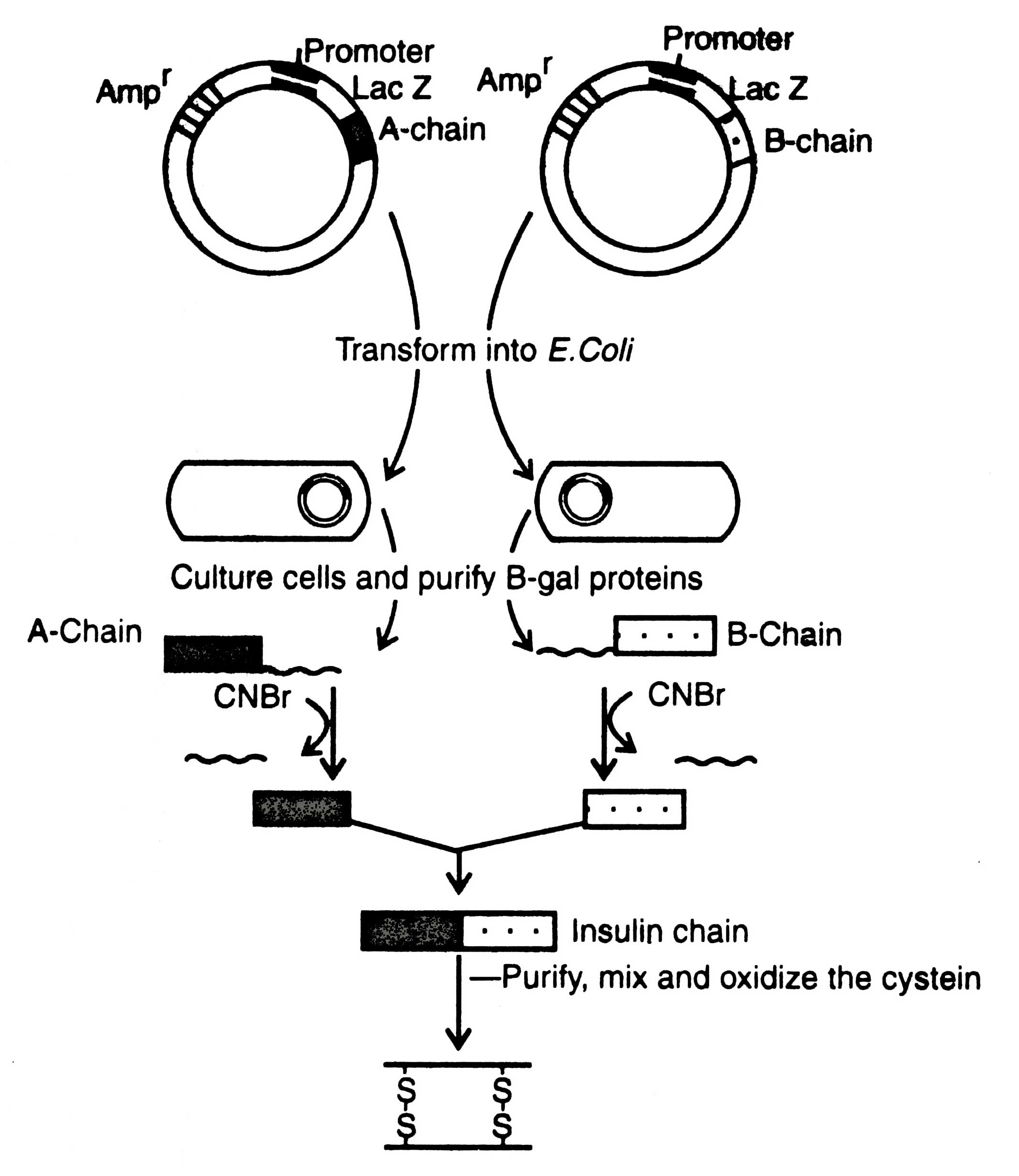
Itakura et. al. (1977) chemically synthesized DNA sequence for two chains, A and B, of insulin and separately inserted into two pBR322 plasmids by the side of b-galactosidase gene. The recombinant plasmids were separately transferred into E coli cells which secreted fused b-galactosidase - A chain and b- galactosidase - B chain separately. These chains were isolated by detaching from b-glactosidase in pure form in a amount of about 10 mg/24 g of healthy and transformed cells (Sasson, 1984). Production of recombinant insulin is shown in Fig. 5.2.
Detachment of proinsulin could be possible when an extra methionine codon was added at the N-terminus of each gene for A and B chains. The two chains (A and B) were joined in vitro to reconstitute the native insulin by sulphonating the two peptides with sodium disulphonate and sodium sulphite.
Somatotropin
Somatotropin, the hGH, is secreted by the anterior lobe of pituitary glands which consists of 191 amino acid units. Its secretion is regulated by two other hormones (somatostatin and growth hormone releasing hormone) produced by hypothalamus. Deficiency of somatotropin in about 3% cases is of hereditary. It has been estimated to about 1 child in 5,000.
Turner's syndrome is one of the most common chromosome disorders in girls and it is characterized by short stature and non-functioning of ovaries affecting approximately 1 in 2,500 live female birth. The extraction of somatotropin pharmaceutically from the pituitary glands could not meet annual demand of this hormone. Biosynthesis of somatotropin was achieved through gene cloning procedures.
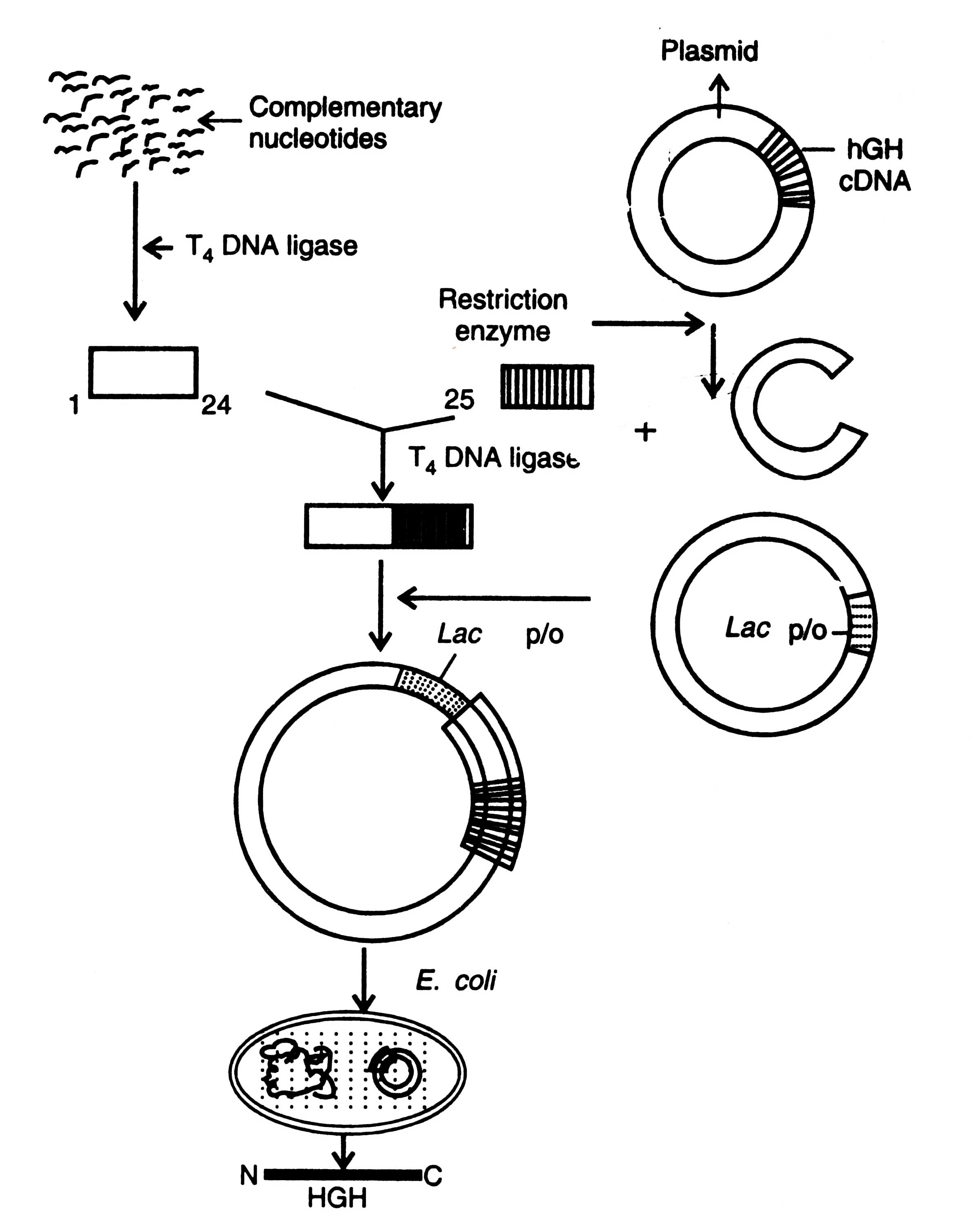
Double stranded cDNAs were produced from mRNA precursor of hGH which was then incorporated into bacterial cells where it expressed in non-precursor form. Bacteria were unable to convert peptide into biologically active form. A recombinant plasmid containing a full length hGH cDNA (which fails to express) is cleaved with restriction enzymes that release a fragment containing the complete hGH coding sequence after codon 24 (Fig. 5.3).
About 100,000 molecules of hormone per cell of E. coli have been produced (Newmark, 1979). One of the major difficulties was that at the N-end of polypeptide an extra methionine, the met-hGW, was attached. Methods are developed to remove methionine from the met-hGW molecules.
Somatostatin, a 14 residue polypeptide hormone is synthesized in the hypothalamus. It is the first polypeptide which was expressed in E. coli as part of the fusion peptide (Itakura et at, 1977) which inhibited the secretion of growth hormone, glucagon and insulin. It does not contain any internal methionine. Eight single stranded DNA segments were synthesized chemically which were annealed in an overlapping manner to form a double stranded DNA (the synthetic gene). It had single stranded projections at the each end as the same are formed by Eco RI. The synthesized gene contained 51 base pairs which were terminated by two non-sense (stop) codon and preceded by a methioine codon as below:
ATG - (42 base pairs encoding somatostatin) - TGATAG.
Two plasmids, pSOM I and pSOM 11-3, were constructed. The synthetic gene was introduced into E. coli b-galactosidase gene at different sites.
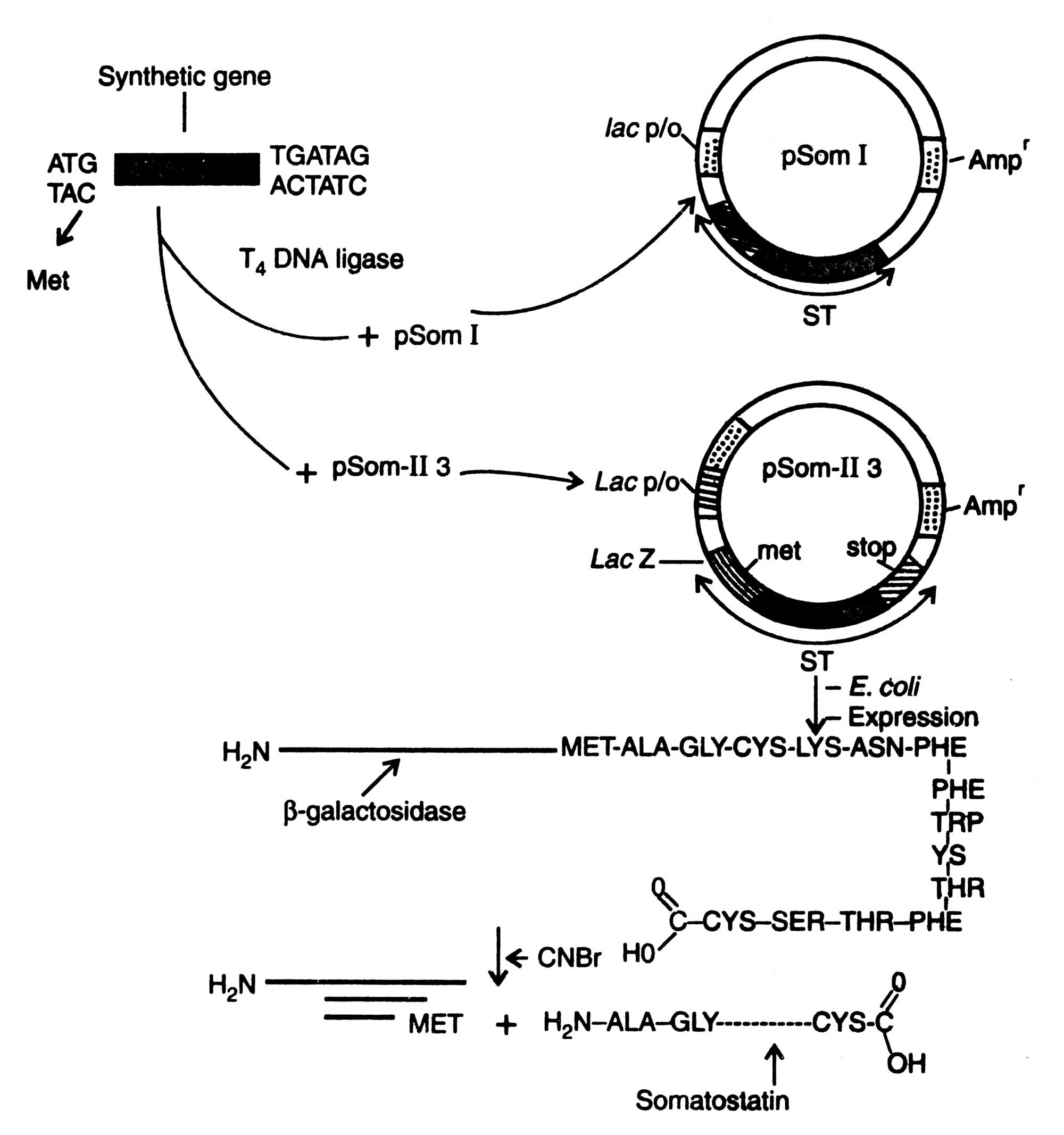
Fig. 5.4. Synthesis of somatostatin, Lac P/O, lactose promoter/operator, ST, somatostatin; Amp, ampicillin resistance.
The chemically synthesized gene was inserted down stream from the lac promoter in such a way that the gene fusion should have specified a polypeptide in which the first 7 amino acids of b-galactosidase were fused to somatostatin. But the somatostatin was not detected in transformed bacteria; possibly it was degraded in E. coli (Glover, 1994). An alternative plasmid, pSOM II-3, was constructed which had the both lac promoter /operater and lacL regions. The lacZ gene encodes peptide of b-galactosidase. If the resulting frame of lacL is maintained after inserting a DNA, a fusion peptide is produced. The plasmid was cleaved in the lacL segment by restriction enzyme (Fig. 5.4). The synthetic gene was inserted into the plasmid at Eco RI site near C-terminus of b-galactosidase. The plasmid in the transformed bacterium directs the synthesis of a fused protein consisting of NH2- termined segment of b-galactosidase fragment coupled by methionine to somatostatin. It was stabilized from proteolytic degradation by b-galactosidase moiety (Glover, 1984). This fused protein was purified and treated with cyanogen bromide (CNBr) which cleaves only protein at the carboxyl side of the methionine. Thus, the methionine linker remains attached to b-galactosidase fragment, and somatostatin was released. Now, it has become possible to inhibit the degradation of foreign protein in E. coli by introduction of protease inhibition (PIN) gene of T4 phage.
β-endorphin (30 amino acid long neuropeptide with opiate activity) is another growth hormone which was expressed in genetically engineered E. coli cells. Shine et al. (1980) integrated DNA sequences of b-endorphin, obtained from mRNA, adjacent to b-glactosidase genes on plasmid. The mRNA contained large precursor of protein that consisted of, besides b-endorphin, the hormones a-melanotropin, corticotropin, b-lipotropin and b-melanotropin. The b-endorphin is cleaved from C-terminus of the precursor peptide. In this way, the transformed bacteria produced an insoluble fusion protein between b-galactosidase and b-endorphin. b-endorphin can be removed from the hybrid protein by tripsin which cleaves only at arginin residue. Before doing so, internal lysines are protected from trypsinization by citraconylation as below:
| NH3 - b - glactosidase - b - melanotropin - b endorphin – COOH |
||
| Citraconylation | ||
| Trypsin | ||
| b - galactosidase + b - endorphin |
||