Haplontic or Zygotic Life Cycle in Algae
This cycle is characterized by a single predominant haploid vegetative phase, with the meiosis taking place upon germination of the zygote. Chlamydomonas (Chlorophyta) (Figure 1.19) exhibits this type of life cycle.
Diplontic or Gametic Life Cycle
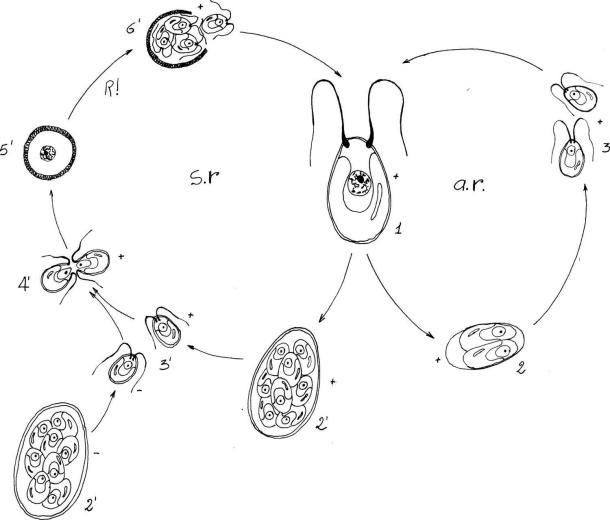
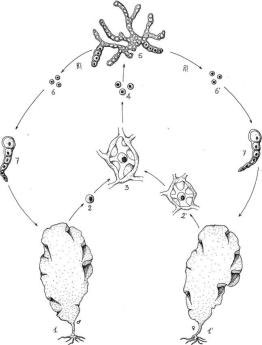
This cycle has a single predominant vegetative diploid phase, and the meiosis gives rise to haploid gametes. Diatoms (Figure 1.20) and Fucus (Heterokontophyta) (Figure 1.21) have a diplontic cycle.
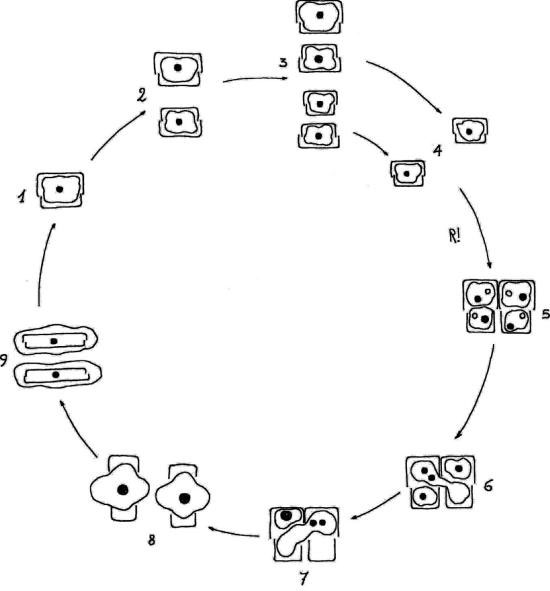
FIGURE 1.20 Life cycle of a diatom: 1, vegetative cell; 2, 3, vegetative cell division; 4, minimum cell size; 5, gametogenesis; 6, 7, fertilization; 8, auxospores; 9, initial cells. R!, meiosis.
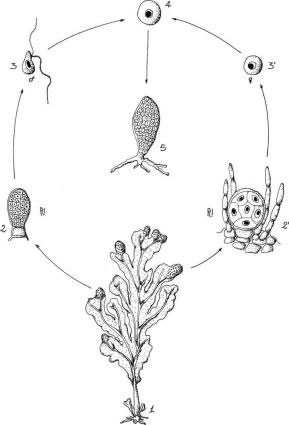
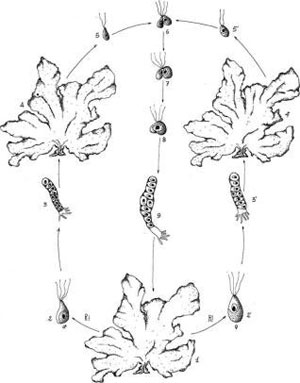
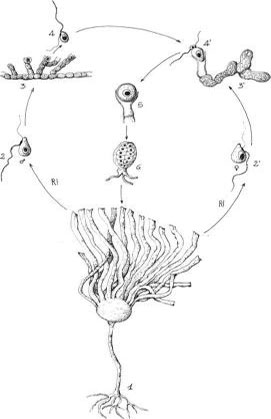
These cycles present an alternation of generation between two different phases consisting in a haploid gametophyte and a diploid sporophyte. The gametophyte produces gametes by mitosis; the sporophyte produces spores through meiosis. Alternation of generation in the algae can be isomorphic, in which the two phases are morphologically identical as in Ulva (Chlorophyta) (Figure 1.22) or heteromorphic, with the predominance of the sporophyte as in Laminaria (Heterokontophyta) (Figure 1.23) or with the predominance of the gametophyte as in Porphyra (Rhodophyta) (Figure 1.24).