Biotechnology Methods / Molecular Biology
Nucleotide Composition of RNA
Materials
- RNA sample
- 1 N and 0.1 N HCl
- Boiling water bath
- Whatman #1 filter paper (for chromatography)
- Chromatography tank
- 20-µL micropipette
- Acetic acid:butanol:water (15:60:25) solvent
- UV light source
- UV spectrophotometer
Procedure
- Place a portion of your RNA sample (approximately 40 mg, hydrated) into
a heavy-walled pyrex test tube. Add 1.0 mL of 1 N HCl and seal the tube.
- Heat the tube in a boiling water bath for 1 hour.
- Cool the tube, open it, and place the contents into a centrifuge tube.
Centrifuge the contents at 2000 rpm in a clinical centrifuge to remove any
insoluble residue. The supernatant contains your hydrolyzed RNA.
- Prepare Whatman filter paper No. 1 for standard one-dimensional chromatography.
- Using a micropipette, spot 20 µL of your hydrolyzate onto the paper, being
careful to keep the spots as small as possible (repeated small drops are
better than 1 large drop). Allow the spots to completely dry before proceeding.
- Place the paper chromatogram into your chromatography tank and add the
solvent (acetic acid:butanol:water). Allow the system to function for an
appropriate time (approximately 36 hours for a 20-cm descending strip of
Whatman #1). Remove the paper and dry it in a circulating air oven at
40°C for about 2 hours.
- Locate the spots of nucleotides by their fluorescence under an ultraviolet
(UV) light source. Expose the paper chromatogram to a UV light source
and outline the spots using a light pencil. The order of migration from the
point of origin is guanine (light blue fluorescence), adenine, cytilic acid,
and finally, uridylic acid.
Do not look directly at the UV light source. Use a cabinet designed to
shield from harmful UV radiation.
- After carefully marking the spots, cut them out with scissors and place the
paper cutouts into separately labeled 15-mL conical centrifuge tubes. Add
5.0 mL of 0.1 N HCl to each tube and allow the tubes to sit for several
hours to elute the nucleotides from the paper.
- Pack down the paper with a glass rod (centrifuge in a clinical centrifuge
if necessary) and remove an aliquot of the liquid for spectrophotometric
assay.
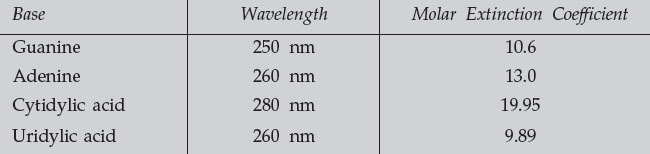
- Measure the absorbance of each of the four nucleotides at the indicated UV
wavelength (having first blanked the instrument with 0.1 N HCl).
- Use the molar extinction coefficients to determine the concentration of each
base in the sample. Calculate the percent composition of each base, and
the purine/pyrimidine ratio.
Support our developers

More in this section